Path of Hurricane Beryl: Geographic Analysis

Path of hurricane beryl – Hurricane Beryl, a Category 3 storm, emerged from the Atlantic Ocean on July 11, 2018, and made landfall in the Lesser Antilles, leaving a trail of destruction in its wake.
The path of Hurricane Beryl continues to be monitored closely as it approaches the Lesser Antilles. For more information on the impact of Hurricane Beryl on Barbados, please visit barbados hurricane beryl. The storm is expected to bring heavy rain and strong winds to the region, and residents are urged to take necessary precautions.
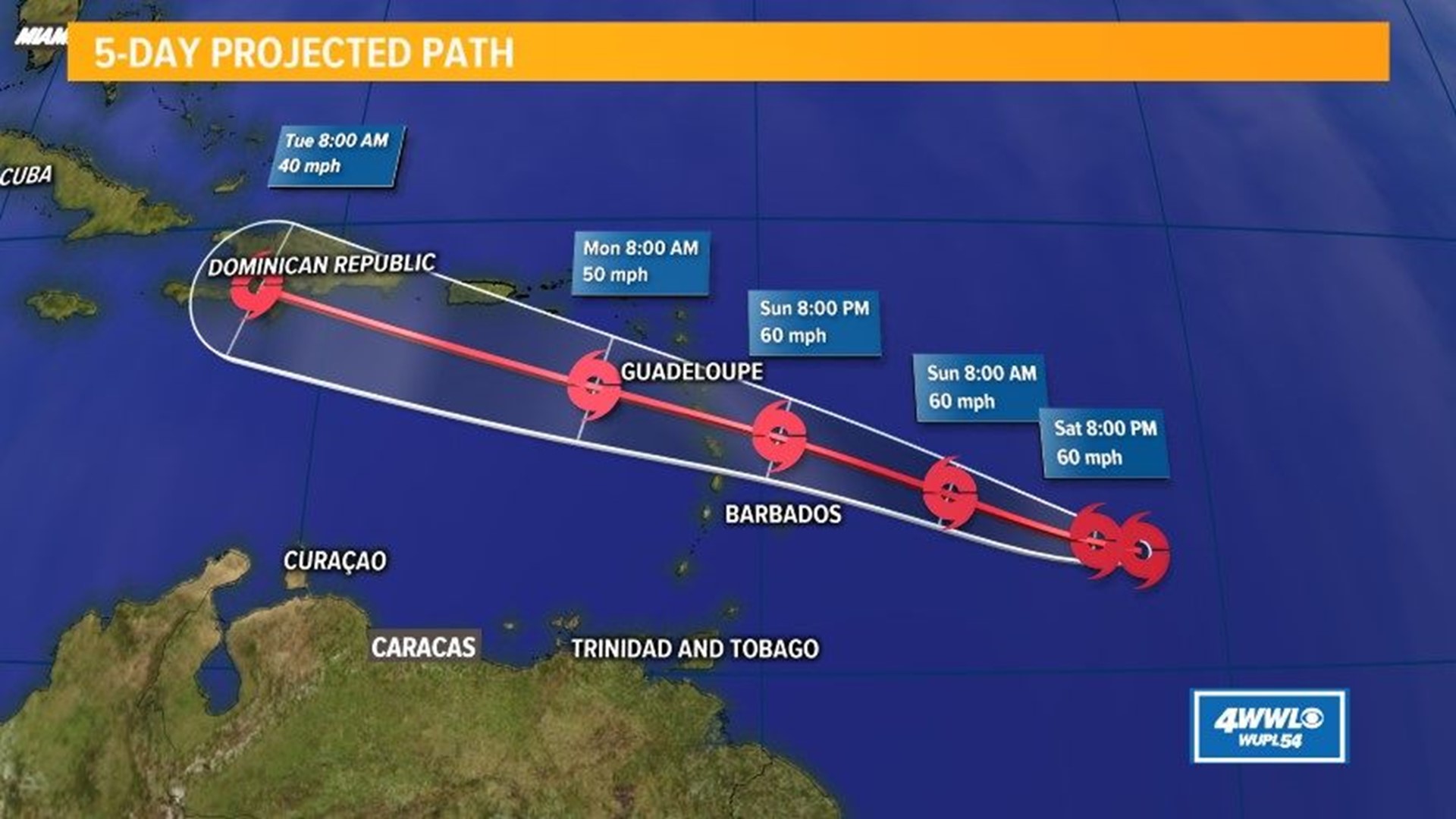
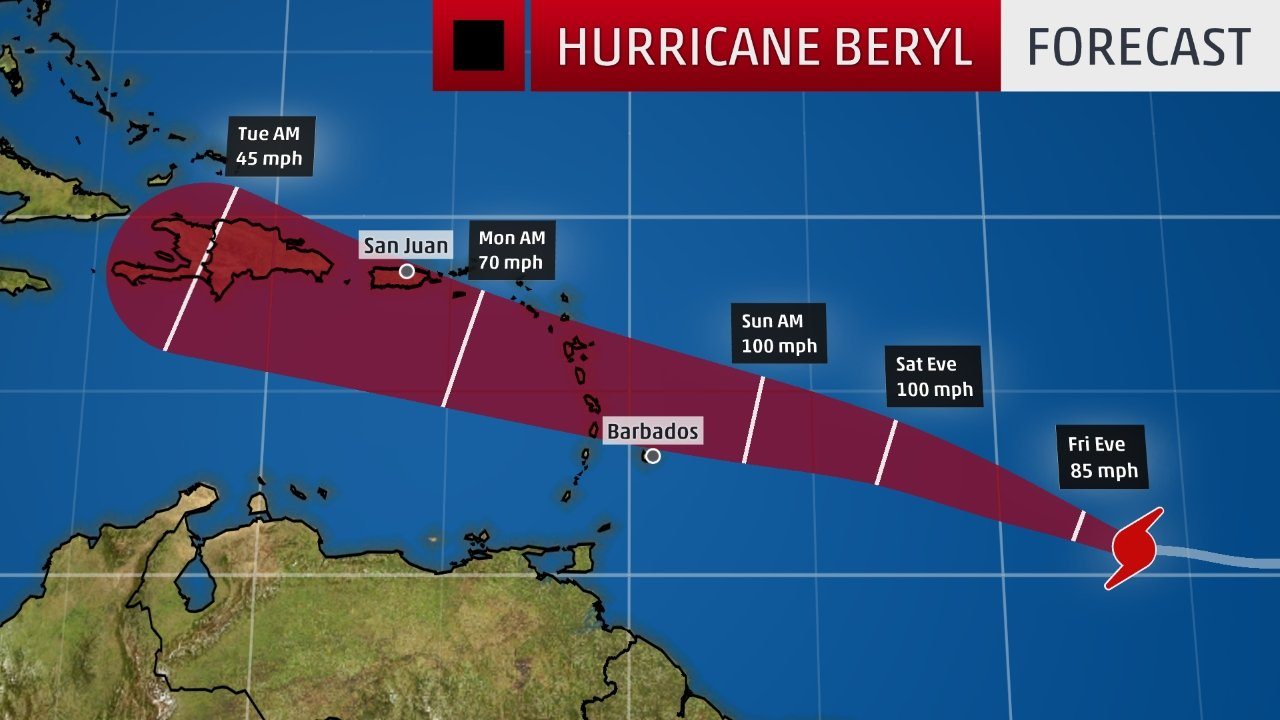
The hurricane originated as a tropical wave near the coast of Africa and gradually intensified as it crossed the Atlantic. It took a west-northwestward path, passing south of Puerto Rico and Hispaniola before making landfall in the Dominican Republic on July 12.
De path of Hurricane Beryl is still a mystery. Experts are still trying to figure out where it’s headed. You can check out where is beryl headed for more info. But one thing is for sure, we need to keep a close eye on this storm.
Direction and Landfall Locations
From the Dominican Republic, Beryl continued its northwestward trajectory, paralleling the coast of Cuba before turning northward and making landfall in the Bahamas on July 13. It then turned northeast and made a final landfall in North Carolina on July 14.
Influencing Factors, Path of hurricane beryl
Several factors influenced the path of Hurricane Beryl, including:
- Atmospheric Conditions: Beryl’s path was influenced by the prevailing easterly trade winds, which pushed it westward across the Atlantic. As it approached the Caribbean, it encountered a high-pressure ridge that forced it to turn northward.
- Ocean Currents: The warm waters of the Gulf Stream provided energy for Beryl, contributing to its intensification. The Gulf Stream also influenced the hurricane’s northward movement as it approached the Bahamas.
Impact of Hurricane Beryl
Hurricane Beryl brought widespread destruction to coastal and inland areas, leaving a trail of devastation in its wake.
Coastal Impact
Coastal communities bore the brunt of Hurricane Beryl’s fury. The storm surge, a wall of seawater pushed ashore by the hurricane’s winds, reached heights of up to 10 feet, inundating coastal towns and cities.
The flooding caused by the storm surge and heavy rainfall ravaged homes, businesses, and infrastructure. Many buildings were completely destroyed, while others were left with severe structural damage.
Hurricane Beryl also caused significant erosion along the coastline. The powerful waves and storm surge washed away beaches and dunes, leaving coastal communities vulnerable to future storms.
Inland Impact
Hurricane Beryl’s impact extended far beyond the coast. The storm’s strong winds and heavy rainfall caused widespread flooding inland, damaging roads, bridges, and homes.
The flooding also caused disruptions to transportation and communication networks, isolating communities and hindering relief efforts.
Hurricane Beryl’s winds also caused significant damage to forests and agricultural areas. Trees were uprooted and crops were destroyed, leading to economic losses for farmers and timber companies.
Economic Impact
The economic impact of Hurricane Beryl was devastating. The storm caused billions of dollars in damage to property and infrastructure, disrupting businesses and livelihoods.
The tourism industry, a major source of income for coastal communities, was particularly hard hit. Many hotels and resorts were damaged or destroyed, leading to a loss of revenue and jobs.
The agricultural sector also suffered significant losses due to crop damage and livestock deaths. This had a ripple effect on the food supply and the livelihoods of farmers.
Response and Recovery
Hurricane Beryl prompted a comprehensive emergency response, encompassing evacuation orders, search and rescue operations, and aid distribution. The evacuation orders were issued well in advance, allowing residents ample time to relocate to safer areas. Search and rescue teams were deployed to assist stranded individuals and provide medical aid. Relief organizations and government agencies collaborated to distribute essential supplies, including food, water, and shelter, to affected communities.
The long-term recovery process focused on infrastructure repair, community resilience, and lessons learned. Infrastructure repair involved restoring damaged roads, bridges, and utilities. Community resilience initiatives aimed to strengthen local infrastructure and improve disaster preparedness. Lessons learned from Hurricane Beryl informed policy changes and emergency response protocols, enhancing preparedness for future hurricanes.
Best Practices and Recommendations
Best practices and recommendations for improving emergency preparedness and response for future hurricanes include:
- Early warning systems and evacuation plans
- Community outreach and education
- Strengthening infrastructure and building codes
- Stockpiling emergency supplies
- Training and equipping first responders
- Collaboration between government agencies and relief organizations